Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, is a common issue for divers, causing pain and discomfort. To prevent it, there are some simple strategies. By following these tips, divers can have a more enjoyable underwater experience.
- Equalizing the pressure in the middle ear is very important. Do this by gently blowing through the nose while pinching it shut. This opens the Eustachian tube and lets air into the middle ear, balancing the pressure. Do this often during descent to stay in equilibrium.
- Good fitting masks and earplugs create a seal around the ear canal, reducing pressure changes that affect the ears. Investing in high-quality diving gear with good insulation is also helpful.
- Stay hydrated before and during diving. This helps the respiratory system stay moist and flexible, making it easier to equalize pressure in the ears. Drinking enough fluids is important for overall health and the body’s natural mechanisms underwater.
- Proper ascent techniques are also essential. Ascending too quickly can lead to barotrauma. Ascend slowly and equalize your ears throughout the ascent. This ensures a smooth transition back to the surface.
Understanding Ear Barotrauma
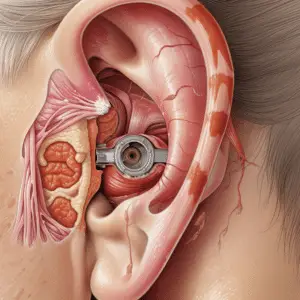
To prevent ear barotrauma while diving, understanding ear barotrauma is crucial. Learn about what ear barotrauma is and the causes and risk factors associated with it.
What is ear barotrauma?
Ear barotrauma is when there’s a sudden pressure change between the outer and middle ear. It can happen during activities like scuba diving, flying, or going up a mountain. It causes pain, discomfort, and can even damage the ear.
Our ears can’t adjust quickly enough, so they become blocked or congested. This leads to fullness and temporary hearing loss. It can also cause dizziness and ringing.
To prevent ear barotrauma, equalize the pressure when you experience rapid altitude or depth changes. Do this by swallowing, yawning, or blowing gently through the nose while pinching it shut. This opens the Eustachian tubes and lets air in or out of the middle ear, reducing pressure.
Severe symptoms like intense pain or bleeding from the ear need medical attention. A professional healthcare provider will assess the condition and give treatment options.
Pro Tip: Be aware of pre-existing conditions like sinus congestion or allergies, as these make you more likely to have ear barotrauma. Check with your healthcare provider before activities with rapid pressure changes.
Causes and risk factors
Ear barotrauma involves the damage or injury to ears due to changes in pressure. Knowing the causes and risks of this condition is key to preventing and managing it correctly.
- Actions such as diving, flying, or cruising at high altitudes can lead to ear barotrauma. The sudden pressure shifts can cause ear discomfort or pain.
- Insufficient pressure balancing in the middle ear can also be a cause. This occurs when the Eustachian tube, which links the middle ear to the throat, is blocked.
- Individuals with allergies, sinusitis, or upper respiratory infections are more prone to ear barotrauma. These issues can affect the Eustachian tube and make it difficult to equalize pressure.
Most cases of ear barotrauma are mild and go away on their own, but some might have serious symptoms or complications. If these worsen or persist, medical help should be sought.
A diver reported a deep dive experience, during which he was regularly equalizing pressure, but then felt intense pain in his ears. After surfacing, he noticed blood coming from one ear. He needed immediate medical attention to treat the ruptured eardrum and avoid more problems.
Knowing the causes and risks of ear barotrauma helps us take precautions and seek care when needed. Being aware of these factors will minimize the chances of experiencing any discomfort or damage to our ears during activities that involve pressure changes.
Prevention Techniques
To prevent ear barotrauma while diving, equip yourself with effective prevention techniques such as equalization techniques, descending and ascending techniques, and proper equipment selection and usage. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, These methods will help you maintain ear health and avoid the discomfort and potential injuries associated with changes in pressure underwater.
Equalization techniques
Check out these common equalization techniques!
- Graphic Equalizer: Modifies overall sound with adjusted frequency bands.
- Parametric Equalizer: Allows fine-tuning of specific frequencies.
- Dynamic Equalizer: Automatically changes settings with input signals.
- Linear Phase EQ: Keeps phase relationships between frequencies accurate.
- Passive Equalizer: Alters signal without active components.
Plus, there’s adaptive filtering. It alters frequency response depending on conditions.
Pro Tip: Analyze the audio/video content carefully. Experiment and adjust to get optimal results.
Valsalva maneuver
Do the Valsalva maneuver to stay safe! Here’s how:
- Pinch your nose shut with your fingers.
- Take a deep breath in.
- Forcefully exhale – lips sealed, nose pinched.
- You’ll feel pressure in your ears and sinuses.
- Release the pressure – open mouth and nose.
It helps normalize pressure imbalances. Useful while scuba diving, flying, or lifting weights.
Warning: Don’t overdo it – may lead to barotrauma or fainting.
Toynbee maneuver
The Toynbee maneuver is a way to help ease pressure in the middle ear. It’s a combo of nose pinching and swallowing. It’s great for activities like scuba diving and flying.
Yawning and swallowing are other techniques to help with ear pressure. These involve opening the mouth wide and contracting throat muscles. It’s an easy way to prevent discomfort from air pressure changes.
Harvard Medical School says that regularly doing the Toynbee maneuver can improve Eustachian tube function. This reduces the risk of ear issues with altitude or water pressure changes.
Frenzel maneuver
The Frenzel maneuver, a vital technique for divers and pilots, equalizes pressure in the ears during abrupt altitudinal changes. To do it right, follow these steps:
- Close your mouth and pinch your nose shut.
- Now exhale gently through your nose. This creates a tiny positive pressure in the nasal passages.
- At the same time, swallow or move your jaw forward and down. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, This’ll open the Eustachian tubes and let air into the middle ear space.
By doing the Frenzel maneuver, you can prevent discomfort and damage caused by unequal pressure. But, remember to get proper training and practice before attempting it.
Take the example of a diver exploring a wreck 30 meters deep. He suddenly felt intense pain due to barotrauma. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, But, he had learned the Frenzel maneuver. So, he quickly executed it underwater. And, in a few seconds his ears popped and the pain subsided, enabling him to continue the dive without any issues. This story shows how important it is to learn and be ready to use techniques like the Frenzel maneuver.
Descending and ascending techniques
- Start by looking at the present. This will give you info on what needs to be altered.
- Set goals that fit your aims. These should be guidelines throughout.
- Analyze the space between the current and desired state. This will help you learn which areas need upgrading and what needs to be done.
- Create an action plan. It should have steps that are easy to track, achievable, relevant, and have a timeline.
- Follow the plan. Stick to the timeline and keep an eye on your progress. Make changes as necessary.
- Evaluate and adjust. Compare the results with your expectations. Adapt or modify if needed.
- Remember: Techniques vary for various circumstances. Get help or use resources when applying them.
Pro Tip: Keep communication lines open. This will help stakeholders stay updated on what’s happening.
Slow and controlled descent
Slow and controlled descent is key to avoiding accidents. To do this:
- Keep a steady pace – no sudden movements. Focus on keeping a consistent speed.
- Keep your body centered – distribute weight evenly.
- Use the right equipment – get good traction shoes.
Every situation is different though. Sarah, a mountaineer, found herself going too fast on the slippery Himalayas. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, She quickly adapted to slow and controlled descent. She adjusted her pace, kept her body centered, and used her good grip shoes. Safely, she reached lower ground.
Slow and controlled descent is essential to stay safe on heights or inclines. It reduces risks and ensures a safe journey.
Proper ear clearing during ascent
Protect your ears from air pressure changes during ascent – it’s vital! Here’s a guide to help:
- Swallow often. It helps balance the pressure between your ears and the environment.
- Yawn wide. It activates the muscles and tubes in your ears, helping regulate pressure.
- Try the Valsalva maneuver. Pinch your nose, then blow air out gently with your mouth closed. This opens the Eustachian tube, balancing ear pressure.
Remember, avoiding discomfort is all about prevention. Use these methods to reduce the chances of pain or damage to your ears.
Pro Tip: Practice these techniques before you even board the aircraft or start ascending. That way, you’ll be ready and get maximum effectiveness.
Equipment selection and usage
When picking equipment, think about what you need for the job. It varies for different tasks, so choose carefully.
Take into account things like weather, humidity, and terrain when selecting gear.
Train users on how to use it safely. Without training, misuse might happen and then accidents can happen too.
Check it often – for damage, wear and tear, and lubricate moving parts. Also, replace any broken bits.
Follow the maker’s instructions. These are there to help with performance and increase safety.
Plus, wear PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) for added security.
Remember, the right selection and use of equipment is about being compliant but more importantly it’s a way to protect yourself and others from harm.
And lastly, set up a routine service schedule. This helps to reduce breakdowns and make it last longer.
Choosing the right mask
Picking the right mask is fundamental to stopping the spread of diseases. Consider these 5 points:
- Material: Choose masks made of top-notch, breathable fabrics, like cotton or microfiber. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, They provide superior filtration and comfort.
- Fit: Make sure the mask fits snuggly over your nose and mouth without any gaps. A good fit gives you a higher level of protection.
- Layers: Look for masks with multiple layers of fabric. This enhances filtration efficiency by trapping more particles.
- Filter pocket: Opt for masks with a built-in filter pocket. You can add extra filters for additional protection against contaminants.
- Certification: Check if the mask has been certified by a reliable testing organization. Certified masks meet specific standards and deliver better filtration.
Also, it’s important to remember that the right mask may vary depending on the situation. Think about risk exposure, duration of use, and local guidelines before making your choice.
To further improve mask effectiveness, here are more tips:
- Proper hygiene: Always wash your hands before handling your mask and don’t touch it while wearing. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, Discard disposable masks after each use.
- Mask maintenance: Clean reusable masks with soap and water regularly, or follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Avoid sharing: Don’t share your mask with others to avoid cross-contamination.
- Breathability: Select a mask that’s both filter efficient and breathable. Masks that restrict airflow too much can cause discomfort.
By following these tips, you can make sure you pick a suitable mask that offers maximum protection against airborne contamination, whilst taking your comfort and safety into account.
Considering a hood or earplugs
Hoods and earplugs can be super helpful for blocking out distractions and unwanted noise. Let’s look at four great points why:
- A hood can shield you from visual interruptions, creating a private space for you to focus.
- Earplugs will reduce loud noises and protect your hearing, creating a serene working environment.
- Both items will act as a sign to others that you’re busy and shouldn’t be disturbed.
- By cutting down external noise, hoods and earplugs aid in deep concentration, which leads to better productivity.
Safety-wise, you should also remember to stay aware of your surroundings. Furthermore, there are many different types of hoods and earplugs available – each designed to fulfill specific needs such as noise cancellation or comfortability.
Here’s a personal story about the advantages of using hoods or earplugs. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, Jane, an author who had trouble focusing in her open office, decided to try out noise-canceling earplugs. They worked amazingly, granting her undisturbed hours of writing. And, thanks to them, she managed to finish all her tasks quickly and with great quality.
Additional Tips
To prevent ear barotrauma while diving, equip yourself with additional tips. Ensure proper ear care before and after dives. Also, consider consulting with a diving professional. These measures provide potential solutions for keeping your ears safe and minimizing the risk of barotrauma during your diving adventures.
Ear care before and after dives
Ear care is essential for scuba diving. Good ear care can avoid issues and complications. Here is a 3-step guide to make sure your ears are taken care of:
- Pre-dive Prep:
- Make sure your ears are clear of blockages (wax, etc). Clean them before diving.
- Use drops designed for divers. Follow instructions.
- If you’ve had ear problems, talk to a doctor before diving.
- Ear Equalization:
- Learn and practice techniques like Valsalva or Toynbee to equalize pressure.
- Do this often during ascent and descent for safe barotrauma.
- Post-dive Care:
- Rinse your ears with fresh water after each dive to get rid of salt or chlorine.
- Don’t use cotton swabs or objects to clean your ears. They could push wax in or cause injury.
- If you feel pain, discomfort or hearing changes, get medical help fast.
Some divers may be more prone to ear problems. Wearing specialized ear protection can give extra protection and peace of mind.
I remember a diver who didn’t do proper ear care. As we went deeper, he had bad pain and couldn’t equalize. He had to quit the dive. This showed me how essential it is to follow ear care practices to have an enjoyable dive.
Consulting with a diving professional
When consulting with a diving pro, speak openly about any worries, limits, and expectations. They can tailor suggestions to you specifically. Plus, they can judge your physical fitness and give advice on training programs or exercises for better underwater stamina.
It’s vital to comprehend the potential risks linked to different dive sites and weather conditions. A diving pro can provide up-to-date info on local regulations, marine life behavior, and environment changes that could affect your dive.
Always respect the expertise of a diving pro during training or guided dives. Ear Barotrauma Prevention Techniques, Follow their instructions precisely to stay safe in underwater surroundings you’re not familiar with.
Pro Tip: Before any dive, consult with a diving pro to build confidence in your abilities and knowledge. Their guidance will help make your underwater exploration fun and secure.
Conclusion
Preventing ear barotrauma while diving is easy when you take the right precautions. Here are some tips:
- Equalize the ear pressure regularly during descent by blowing air through your nose and swallowing.
- Don’t dive with a cold or sinus congestion.
- Descend and ascend at a slow pace.
- Use earplugs designed for diving to create a barrier between the ear and water.
- Strengthen the muscles surrounding the ears with jaw movements and yawning.
- Stay hydrated before and during dives.
Sophie, a diver, learned this lesson the hard way when she experienced severe ear pain after a deep dive in Egypt. Now she knows the value of taking precautions!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is ear barotrauma?
A: Ear barotrauma is a condition that occurs when there is a difference in pressure between the outer and middle ear, causing discomfort or pain.
Q: How can I prevent ear barotrauma while diving?
A: To prevent ear barotrauma while diving, you can try the following precautions:
- Equalize your ears regularly by swallowing, yawning, or using the Valsalva maneuver.
- Descend and ascend slowly to allow your ears to adjust to pressure changes.
- Avoid diving if you have a cold, sinus congestion, or any ear infection.
- Consider using earplugs or a hood to help regulate pressure.
Q: Can ear barotrauma cause permanent damage?
A: In most cases, ear barotrauma does not cause permanent damage. However, in rare cases, it can lead to complications such as a ruptured eardrum or inner ear barotrauma, which may require medical attention.
Q: Are there any warning signs of ear barotrauma?
A: Yes, some common warning signs of ear barotrauma include ear pain or pressure, muffled or decreased hearing, dizziness, and in severe cases, blood or fluid discharge from the ear.
Q: Can I still dive if I have a history of ear barotrauma?
A: It is advisable to consult with a medical professional if you have a history of ear barotrauma before diving. They can evaluate your condition and provide specific recommendations based on your medical history.
Q: Are there any medications that can help prevent ear barotrauma?
A: There are no specific medications to prevent ear barotrauma. However, if you have underlying conditions such as allergies or sinus congestion, treating those conditions before diving may help reduce the risk of ear barotrauma.
